- Folder Technical News
- Views 394
- Last Updated 23/12/2024
Antioxidants are compounds that can prevent or limit the damage caused by free radicals. Using natural products to supplement your body with antioxidants will benefit your health.
1. Introduction
An antioxidant is a substance or group of compounds found in foods or medicines, that promote health and protect against cell damage caused by free radicals.
Antioxidants are classified into antioxidants of synthetic origin and antioxidants of natural origin.
• Synthetic antioxidants: are chemically synthesized compounds used to help prevent lipid oxidation. Currently, the commonly used compounds are butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), Tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ), Ethoxyquin, propylgallate (PG) and some phenolic compounds.
• Natural antioxidants fall into two main groups: enzymatic antioxidants and non-enzymatic antioxidants.
- Enzyme antioxidants: cannot be found in dietary supplements, they are produced naturally in the body. The main enzymatic antioxidants in the body are:
+ Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is found in most aerobic cells and extracellular fluid.
+ Catalase (CAT) is mainly found in the liver.
+ Glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase are most abundant in the liver.
- Non-enzymatic antioxidants: work by blocking the chain reactions of free radicals including several types: carotenoids, vitamin C, vitamin E, plant polyphenols, and glutathione.
+ Ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
+ Vitamin E (tocopherol and tocotrienols)
- Glutathione
- Polyphenols include several types such as: phenolic compounds (gallic acid, vanillic acid, vanillin aldehyde, cinnamic acid...), Flavonoid, flavone, flavonol, Flavanone, Dihydroflavonol, Flavanol, Chalcone and dihydrochalcone, Isoflavone, Anthocyanidin.
- Coenzymes such as coenzyme Q10 and minerals in the form of metalloenzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) containing Mn, catalase containing Fe, glutathione peroxidase containing Se ...
- Carotenoids are an organic pigment that occurs naturally in plants and photosynthetic organisms, including 600 types of carotenoids, arranged in two groups, xanthophylls, and carotenes such as α-carotene, β-carotene, lutein, canthaxanthin, zeaxanthin, lycopene…
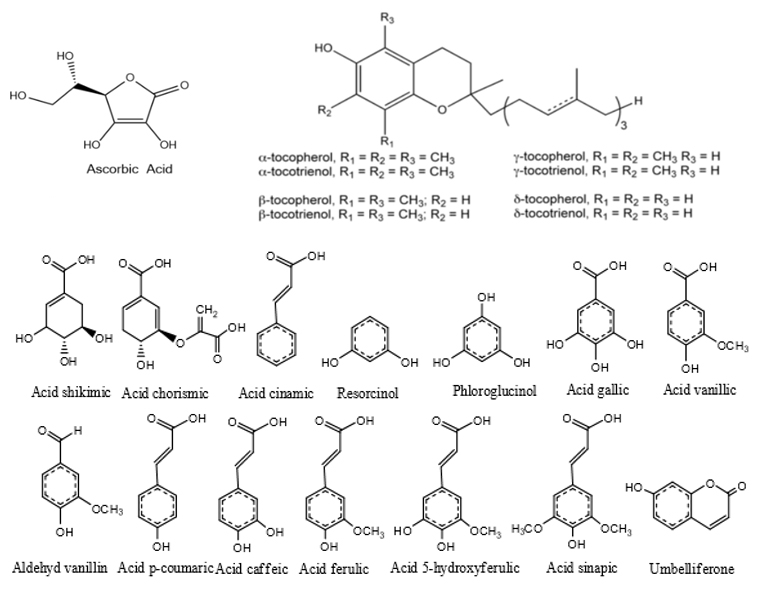
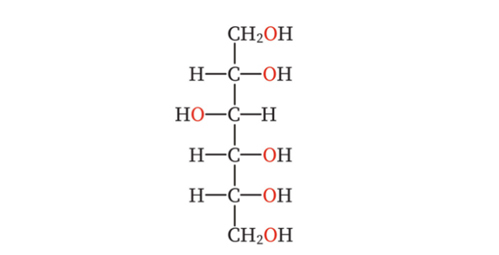
Structure of some natural antioxidants
2. Function of antioxidants
Antioxidants are substances that can prevent or slow damage to cells caused by free radicals, unstable molecules that the body produces as a response to the environment.
Supplementing antioxidants may help reduce vision loss caused by age-related macular degeneration in the elderly. In addition, in cardiovascular diseases, antioxidants contribute to the neutralization of free radicals before they affect LDL (low-density lipoprotein), slowing down the process of atherosclerosis. At the same time, plant-based compounds also help reduce platelet aggregation, regulate cholesterol absorption and synthesis, lower blood pressure, and have anti-inflammatory effects by lowering CRP levels in the blood.
The activity of antioxidants prevents body from many diseases such as cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis, heart failure, myocardial infarction, high blood pressure, ...), cancers, liver diseases, eye diseases (macular degeneration and cataracts), aging, ...
3. Source of Antioxidants
The best sources of antioxidants are plant-based foods, especially fruits and vegetables. There are many studies on antioxidant activity in specific food products as follows:
|
S.No |
Subject |
N |
min - max (mmol Trolox /100g) |
Average (mmol Trolox /100g) |
Median (mmol Trolox /100g) |
|
1 |
Rose, blueberry, strawberry, amla |
119 |
0,06-261,53 |
9,86 |
3,34 |
|
2 |
Coffee, tea, beer, wine, lemonade |
283 |
0,00-1347,83 |
8,30 |
0,60 |
|
3 |
Buckwheat flour, millet |
90 |
0,16-4,84 |
1,09 |
0,89 |
|
4 |
Milk chocolate, dark chocolate |
80 |
0,05-14,98 |
4,93 |
2,33 |
|
5 |
Chese |
86 |
0,00-0,78 |
0,14 |
0,06 |
|
6 |
Chocolate cake |
134 |
0,00-4,10 |
0,45 |
0,20 |
|
7 |
Egg yolk |
12 |
0,00-0,16 |
0,04 |
0,04 |
|
8 |
Margarine, soybean oil, corn oil |
38 |
0,19-1,66 |
0,51 |
0,39 |
|
9 |
Fish |
32 |
0,03-0,65 |
0,11 |
0,08 |
|
10 |
Watermelon |
278 |
0,03-55,52 |
1,25 |
0,69 |
|
11 |
Barley flour |
227 |
0,00-3,31 |
0,34 |
0,18 |
|
12 |
Herbal medicines |
59 |
0,28-2897,11 |
91,72 |
14,18 |
|
13 |
Breast milk, formula milk |
52 |
0,02-18,92 |
0,77 |
0,12 |
|
14 |
Pea |
69 |
0,00-1,97 |
0,48 |
0,27 |
|
15 |
Liver, chicken |
31 |
0,00-0,85 |
0,31 |
0,32 |
|
16 |
Spices |
44 |
0,00-15,54 |
0,77 |
0,15 |
|
17 |
Mixed food |
189 |
0,03-0,73 |
0,19 |
0,16 |
|
18 |
Walnuts, chestnuts, sunflower seeds |
90 |
0,03-33,29 |
4,57 |
0,76 |
|
19 |
Poultry |
50 |
0,05-1,00 |
0,23 |
0,15 |
|
20 |
Biscuits |
66 |
0,00-1,17 |
0,58 |
0,61 |
|
21 |
Tomato sauce |
251 |
0,00-4,67 |
0,63 |
0,41 |
|
22 |
Cloves, Mint, Cinnamons |
425 |
0,08-465,32 |
29,02 |
11,30 |
|
23 |
Kale, Cabbage |
303 |
0,00-48,07 |
0,80 |
0,31 |
|
24 |
Vitamin C, anthocyanin |
131 |
0,00-1052,44 |
98,58 |
3,27 |
The above results show a difference of thousands of times in the antioxidant content of foods. A high level of antioxidant content can be founded in many objects such as: spices, herbs, berry fruits (blueberry, blackberry, strawberry ...), beverages, medicinal herbs, herbs and spices ... Plant-based foods generally have higher antioxidant levels than animal-based and mixed foods, with mean antioxidant values of 0.88, 0.10 and 0.10, respectively. 0.31 mmol/100 g.
Antioxidant supplements: Dietary supplements of antioxidants are necessary, but more is not always good. Consuming too many antioxidants can induce toxic reactions and may even promote rather than prevent oxidative damage – a phenomenon known as the “antioxidant paradox”. Some studies have even shown that high doses of antioxidants increase the risk of death. For this reason, most health professionals recommend that people avoid high-dose antioxidant supplements through supplements as a functional food.
According to the research results of the National Institute for Food Control, the vegetable has a high antioxidant index due to its high content of phenolic compounds. Foods such as beets, red cabbage and carrots will have higher antioxidant activity when not affected by temperature (boiling, steaming).
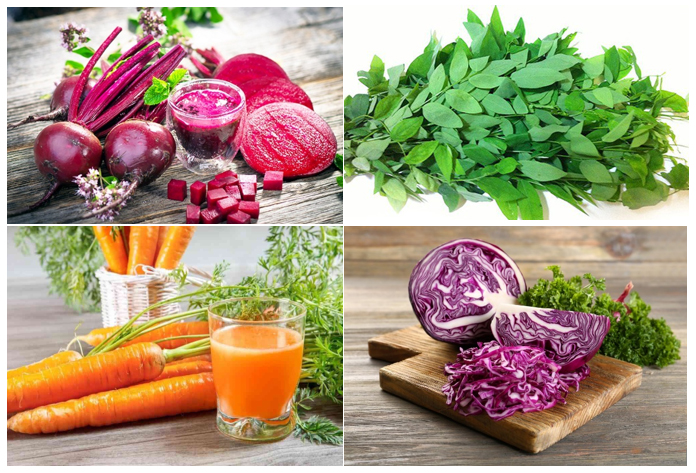

Some foods with high antioxidant activity
At the National Institute for Food Control, we are testing antioxidants using advanced testing methods, ensuring accurate and reliable results with a team of experienced experts, well-equipped facilities that meet all requirements for testing antioxidants in food.
Author. Đỗ Trúc Quỳnh
National Istitute for Food Control
References
1. Atta, E. M., Mohamed, N. H., & Silaev, A. A. A. (2017). Antioxidants: An overview on the natural and synthetic types. European Chemical Bulletin, 6(8), 365-375.
2. Carlsen, M. H., Halvorsen, B. L., Holte, K., Bøhn, S. K., Dragland, S., Sampson, L., ... & Blomhoff, R. (2010). The total antioxidant content of more than 3100 foods, beverages, spices, herbs and supplements used worldwide. Nutrition journal, 9(1), 1-11.