- Folder Technical News
- Views 1671
- Last Updated 12/12/2022
Vitamin C, a natural antioxidant, is essential for the living body but cannot be synthesized by humans. The following article will give you an overview about the role of vitamin C and their content in some common fresh fruits and vegetables, as a reference for you to calculate your daily servings.

1. What is Vitamin C?
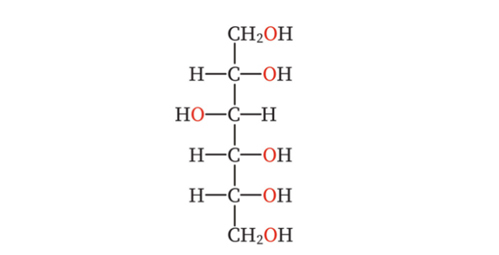
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is the most common and nature antioxidant, which participates in many important life activities of the body. Ascorbic acid which cannot be produced by human body, is found naturally in many fruits and vegetables and made by the kidneys of some animals. Therefore, people take it from diet. Industrially, ascorbic acid is produced through a multi-step process that involves glucose-reducing bacteria and produces ascorbic acid as a sub-product.
Vitamin C can be used in a variety of forms, including salts and esters such as sodium ascorbate, calcium ascorbate, potassium ascorbate, ascorbyl palmitate or ascorbyl stearate, depend on the product ingredients including food products, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
2. The role of vitamin C
* For human:
Vitamin C plays an important role in many metabolic processes.
+ Participate in the collagen formation, which is needed to bind cells and heal wounds, and stabilize blood vessel walls.
+ Take part in energy metabolism
+ Stimulate the activity of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, corpus luteum, blood-forming organs and therefore the role of vitamin C is related to the functions of these organs such as stimulating growth in children, restoring health, increasing labor endurance.
+ Participate in the process of creating antibodies and increasing the body's resistance to infections; stimulates the synthesis of interferon - a substance that prevents the entry of bacteria and viruses into the cell.
+ Be an antioxidant, preventing the formation of free radicals, slowing down the aging process and preventing cardiovascular diseases.
+ Combine with vitamin E to form an important factor in slowing the progression of some cancers.
+ Stimulate the absorption of iron by the small intestine, which is the factor that accelerates red blood cell formation, allowing to reduce the risk of anemia.
* For food
Ascorbic acid is primarily used as an antioxidant and preservative, which can provide many benefits to food products such as slowing down oxidation to help preserve color and freshness since the low pH of ascorbic acid can help inhibit microbial growth. It can be used as a preservative in a wide range of food products, including breads, frozen meats, canned meats, jams and jellies, as well as sauces, etc.
The physicochemical and sensory properties of ascorbic acid make it become an excellent adding ingredient, which can enhance the acidity and the flavor of the product. In particular, natural vitamin C is easily degraded by environmental conditions and external influences, many foods are fortified with vitamin C in many different forms to compensate for the reduced natural vitamin C during production. As a result, ascorbic acid is often added to juices, dried fruits, cereals and other snack foods for this purpose.
3. How much vitamin C is enough?
The amount of vitamin C absorbed and stored by the body is not proportional to the vitamin content in the food, even reduced when the amount of vitamin C in the food is too high. For instance, if a person eats 5 oranges at a time, most of the vitamin C will be wasted and excreted in the urine, even if you eat a lot, the amount of useful vitamin C for the body is still lower than eating one orange regularly after each meal.
The recommended vitamin C requirement for adults is 70-75 mg/day. Smokers need to increase the consumption (100-200 mg/day). Long-term use of high doses of vitamin C can cause diarrhea, nausea, kidney stones and can cause vitamin C deficiency when stopped suddenly.
4. Sources of vitamin C in natural food
This antioxidant is found in many fruits and vegetables. Food containing high level of vitamin C are especially guava, lemon, orange, grapefruit, watermelon, tomato, cabbage and broccoli. The talbe below will give some information about the average of vitamin C content in some common vegetables and fruits.
Table 1. The content of vitamin C in some fruits and vegetables
| Cải bắp - 30 mg/100g | Su hào - 40 mg/100g |
| Cải sen - 51 mg/100g | Thìa là - 63 mg/100g |
| Cần tây - 150 mg/100g | Cam - 40 mg/100g |
| Đậu cove - 25 mg/100g | Dưa bở - 38 mg/100g |
| Giá đậu xanh - 10 mg/100g | Dứa ta - 24 mg/100g |
| Rau diếp - 30 mg/100g | Đu đủ chín - 54 mg/100g |
| Rau dền đỏ - 89 mg/100g | Mít dai, mật - 5 mg/100g |
| Kinh giới - 110 mg/100g | Xoài - 30 mg/100g |
| Bắp cải đỏ - 60 mg/100g | Ổi - 62 mg/100g |
| Cải soong - 69 mg/100g | Táo tây - 7 mg/100g |
| Củ cải trắng - 30 mg/100g | Na - 36 mg/100g |
| Đậu đũa - 22 mg/100g | Quýt - 55 mg/100g |
| Hành lá - 60 mg/100g | Vải - 36 mg/100g |
| Rau đay - 77 mg/100g | Rau muống - 23 mg/100g |
| Rau dền trắng - 27 mg/100g | Rau xà lách - 15 mg/100g |
| Mùng tơi - 72 mg/100g | Xúp lơ - 70 mg/100g |
| Cải thìa - 26 mg/100g | Bưởi - 95 mg/100g |
| Đậu Hà lan - 27 mg/100g | Chanh - 40 mg/100g |
| Hẹ lá - 19 mg/100g | Dâu tây - 67 mg/100g |
| Rau dền - 35 mg/100g | Dứa tây - 26 mg/100g |
| Rau húng - 27 mg/100g | Hồng đỏ - 16 mg/100g |
| Rau mùi - 140 mg/100g | Nhãn - 58 mg/100g |
| Mùi tàu - 177 mg/100g | Nho - 45 mg/100g |
| Rau ngót - 185 mg/100g | Táo ta - 24 mg/100g |
| Rau dăm - 57 mg/100g |
References
1. Thomas, D.L. (2019) Sources of vitamin C, News. Available at: https://www.news medical.net/health/Sources-of-Vitamin-C.aspx (Accessed: December 6, 2022).
2. Vitamin C (2020) Mayo Clinic. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-vitamin-c/art-20363932 (Accessed: December 6, 2022).