- Folder Technical News
- Views 1750
- Last Updated 24/12/2024
Hạt tiêu là một loài cây leo họ Piperaceae, được trồng để lấy quả. Đây là một loại gia vị phổ biến được sử dụng trong món ăn để gia tăng hương vị. Độ cay của hạt tiêu là do hợp chất hóa học piperin, một loại alkaloid có chức năng như chất chống oxy hóa có lợi cho sức khỏe con người.
Black pepper is a type of vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit. This a popular condiments added in food to enhance flavour. The spiciness of pepper is due to the chemical compound of piperine, and alkaloid that functions as an antioxidant beneficial to human health.
1. Black pepper and Piperine in peppercorns
Piperine is a natural chemical compound found in pepper. It is an alkaloid with a chemical structure similar to morphine and quinine. Piperine is responsible for the spiciness of pepper, and together with the essentioal oil compounds (monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, phenylpropanoids), it creates the distinctive flavor and aroma of pepper.
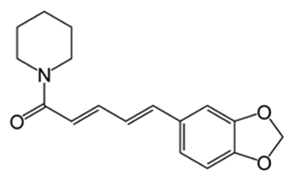
Figure 1. Structural Formula ofPiperine
Pepper contains 2-7.4% piperine, with the variation in content depending on factors such as the cultivation region, time, climate, etc., and the type of pepper plant. Some types of pepper are distinguished by their processing methods:

Figure 2. Some types of peppercorns based on processing method
Black Pepper: The most common type of pepper in Vietnam. Black pepper is produced from ripe or green peppercorns, dried, with a firm and hard surface, and a black color. This type of pepper retains its spiciness, but it is not too intense, with a mild aroma that enhances the heat in dishes.
White Pepper: It has an ivory-white color, slightly yellowish, and a smooth surface. This pepper is made by removing the outer skin. In terms of flavor, white pepper is much spicier than black pepper but has less aroma. Additionally, white pepper contains a higher amount of oil than black pepper.
Green Pepper: This is fresh, unripe pepper, with a mild spiciness and a moderate fragrance, making it very easy to use. Green pepper is commonly used in stews and soups to reduce unpleasant odors.
2. Black Pepper’s uses
Black pepper (Piper nigrum) has been used for many years as a food source, spice, and in traditional medicine as a remedy. Piperine exhibits various pharmacological effects such as anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, cardiovascular and liver protection, antibacterial, and immune-modulating properties in different studies.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with metabolic disorders (MASLD), a group of conditions characterized by fat accumulation in the liver. Common causes include obesity, insulin resistance, and diabetes. Some studies suggest that piperine, combined with curcumin, as a supplement can improve liver function in individuals diagnosed with MASLD. People supplemented with piperine and curcumin had significantly lower blood liver enzyme levels and less severe MASLD. Additionally, total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (considered "bad" cholesterol) were significantly reduced in individuals with metabolic syndrome, along with lower blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, and improved liver enzymes.
- Using Pepper safely
Pepper in the amounts commonly found in food is considered safe.
- High doses of black pepper can cause a burning sensation in the throat or acid reflux.
- The safe amount of black pepper for pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, or children has not been studied.
- The active compound in pepper may slow down the blood clotting process. High doses can lead to bleeding. Therefore, it is recommended to stop supplementing with piperine two weeks before undergoing any surgery.
- People with diabetes should closely monitor their blood sugar levels, as piperine may lower blood sugar levels.
- People with gastrointestinal (GI) disorders may have difficulty tolerating pepper.
- Piperine’s Method of Analysis
Currently, the National Institute for Food Safety Control is using the High-Performance Liquid Chromatography method with PDA detector to analyze piperine. This method has been accredited under ISO/IEC 17011:2017. With good specificity, the detection limit and quantification limit are 3.0 mg/kg and 10.0 mg/kg, respectively. This method is suitable for analyzing piperine content in pepper as well as in food products containing pepper, such as essential oils, dietary supplements, and functional foods.
In addition to its testing activities, the National Institute for Food Safety Control also offers training courses on testing methods, equipment calibration services, provision of standard samples, reference materials, interlaboratory comparison programs, and proficiency testing. For more information, please contact the Institute at the following address:
• Headquarter: Center of Technical and Scientific Services–National Institute of Food Safety Control
Address: 65 Pham Than Duat, Mai Dich, Cau Giay, Ha Noi
Hotline: 085 929 9595
Email: baogia@nifc.gov.vn/ nhanmau@nifc.gov.vn
• Traning Services: Center of Technical and Scientific Services–National Institute of Food Safety Control
Address: 65 Pham Than Duat, Mai Dich Ward, Cau Giay District, Hanoi
• Instruments Calibrations
Ms. Nguyễn Thị Hà Bình
Địa chỉ: 65 Phạm Than Duat, Mai Dich, Cau Giay, Ha Noi
Hotline: 098 8479022
Email: calib@nifc.gov.vn - habinhsp86@gmail.com
• Standards Samples: Center of Technical and Scientific Services
Address: 65 Pham Than Duat - Mai Dich - Cau Giay - Ha Noi
Hotline: 024 3226 2251/0983 739 653 (Ms Thuy)
Email: ptp.rm@nifc.gov.vn
• Hồ Chí Minh City Representative Office
Address: Tan Cang - Cat Lai Port, Room A102, Gate B, Cat Lai Port, 1295B Nguyen Thi Dinh, Cat Lai Ward, Thu Duc City, Ho Chi Minh City
Tel: 028.37.400.888/ Hotline: 0918.959.678 (Mr. Nghi)
Email: vpsg@nifc.gov.vn
• Hải Phòng Representative Office
Address: 1 Ngo Quyen, Hai Phong City
Tel: 0225.8830316/ Hotline: 0983.300.226 (Ms. Thuong)
Email: vphp@nifc.gov.vn
Author: Nguyen Van Khoa – Department of Research and Development
National Insitute of Food Safety Control
References:
[1] Joon-Goo Lee, Young Chae, Youngjae Shin and Young-Jun Kim (2020), "Chemical composition and antioxidant capacity of black pepper pericarp".Applied Biological Chemistry, Article number: 35.
[2] Iahtisham-Ul Haq,Iahtisham-Ul Haq, Muhammad Imran, Muhammad Nadeem et al (2020),"Piperine: A review of its biological effects".Phytotherapy Research, Volume 35, Issue 2, p.680-700.
[3] Jennifer Lefton, MS, RD/N, CNSC, FAND (2023), “What to Know About Black Pepper and Piperine Supplements”. Verywell health.
[4] Ankita Khismatrao et al (2018), "Development and Validation of RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Curcumin and Piperine", International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics, Vol 10, Issue 5.