- Folder Technical News
- Views 2674
- Last Updated 18/07/2024
Food poisoning is a serious global public health issue. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that there are around 600 million cases of foodborne illnesses each year, resulting in 420,000 deaths. In addition to toxins and chemicals, microorganisms are also a major causative agent of food poisoning. The use of appropriate methods to analyze the microbial agents responsible is crucial. Let's explore the syndromic testing method used to analyze the culprits of food poisoning with the National Institute of Food Safety Inspection.
1/ Traditional Culture-based Methods
Microbial culturing is often considered the "gold standard" in food microbiology analysis. The traditional culture-based method is based on the growth and formation of bacterial colonies in a laboratory environment. The advantages of the culture-based method include:
- Sensitivity - It can detect and quantify the microorganisms present in food.
- Cost-effective - It is an economical and easy-to-perform method.
- Comprehensive information - It provides details on the quality, quantity, and types of living microorganisms in the food.
However, the traditional culture-based method often takes several days to identify the pathogenic microorganisms, as it requires multiple steps such as pre-enrichment, selective enrichment, culturing on selective media, and further biochemical and serological confirmations (Figure 1).
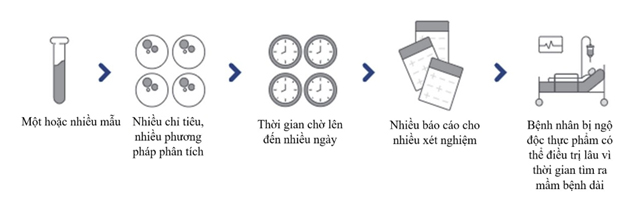
Figure 1: Challenges faced by physicians and healthcare professionals in managing outbreaks or patients with food poisoning
In addition, the symptoms of food poisoning or gastrointestinal infections can overlap, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and bloody stool. This makes accurate diagnosis a challenge. This is a challenge that physicians and healthcare professionals must face when managing outbreaks or patients with food poisoning, as they often have to rely on slow tests and insufficient screening methods to identify the causative agents.
2/ Syndromic Testing - A Rapid Screening Method to Identify the Culprit of Food Poisoning
Over the past two decades, new molecular diagnostic methods have led to significant advancements in the field of clinical microbiology. A prominent example is syndromic testing, which is used to analyze the causative agents of diseases with similar symptoms in patients, such as diarrhea, nausea, fever, and discomfort, and provides rapid and accurate results.
In June 2024, the UK Health Security Agency announced a Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) outbreak affecting over 200 people due to the consumption of sandwiches and salads from supermarkets. Hospitals in the United Kingdom utilized syndromic testing techniques (Figure 2) to quickly screen and diagnose the cause of the outbreak, in combination with whole-genome sequencing to identify any additional pathogens.
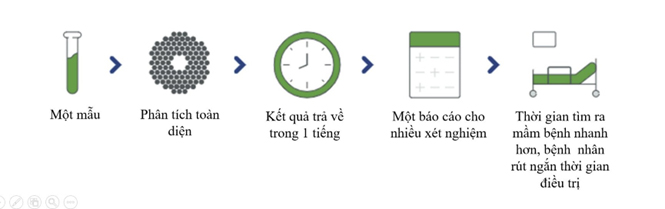
Figure 2: Syndromic testing approach for rapid identification of the causative agent in a foodborne illness outbreak
3/ The Principle of Syndromic Testing
The syndromic testing method employs a multiplex real-time PCR reaction, a widely used technique in molecular biology analysis and diagnosis. This approach allows for the simultaneous detection and quantification of multiple target nucleotide sequences in a single PCR reaction.
In the reaction tube, specific primer and probe sets will simultaneously amplify different target nucleotide sequences. This process is monitored in real-time through the detection of fluorescent signals, where the intensity of the fluorescent signal is proportional to the number of target copies present. The computer software then analyzes the fluorescent signals and determines the concentration of each target (Figure 3).
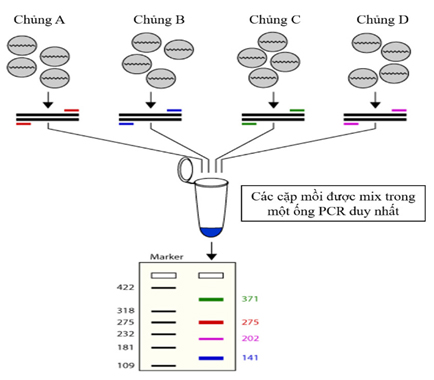
Figure 3: Illustration of the multiplex real-time PCR process in syndromic testing
Multiplex real-time PCR can detect and quantify multiple targets simultaneously, which saves time and cost; it minimizes the risk of false positives and false negatives by using multiple specific primer and probe sets for each target; and it can provide accurate estimates of the copy number for each target.
4/ Foodborne pathogens and gastrointestinal infections that can be detected by syndromic testing:
Currently, syndromic testing can rapidly and accurately detect many infectious agents causing gastrointestinal infections, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites (Table 1).
Table 1: List of microorganisms that can be detected by syndromic testing
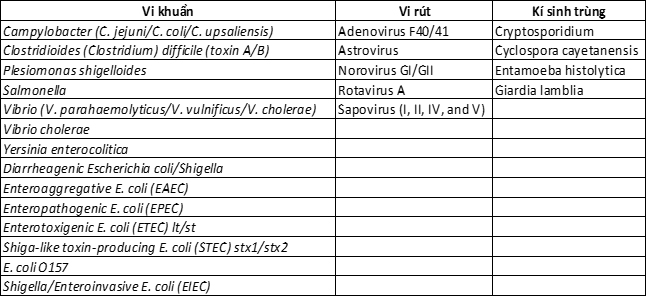
In addition to traditional methods, the National Institute of Food Control is applying syndromic testing techniques to quickly diagnose the causes of food poisoning, followed by confirmation using traditional methods. This approach accelerates the microbiological analysis process, shortens the turnaround time for preliminary results, and minimizes the impact of foodborne illnesses on consumer health and life.
Author: Ngoc Ha Pham – National Institute for Food Control
Reference
[1] “BIOFIRE® FILMARRAY® Gastrointestinal Panel,” bioMérieux Website. Accessed: Jun. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.biomerieux.com/corp/en/our-offer/clinical-products/biofire-filmarray-gastrointestinal-panel.html
[2] “Syndromic Tests For Infectious Disease Diagnostics | QIAGEN.” Accessed: Jun. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available: http://www.qiagen.com/us/applications/syndromic-testing
[3] “Gastrointestinal Infections – Genetic Signatures AU.” Accessed: Jun. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://geneticsignatures.com/au/our-products/gastrointestinal-infections/
[4] “Xét nghiệm Hội chứng bằng kỹ thuật Realtime PCR đa mồi (Syndromic Testing): Bước tiến mới trong xét nghiệm sàng lọc và điều trị | Vinmec.” Accessed: Jun. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.vinmec.com/vi/tin-tuc/hoat-dong-benh-vien/xet-nghiem-hoi-chung-bang-ky-thuat-realtime-pcr-da-moi-syndromic-testing-buoc-tien-moi-trong-xet-nghiem-sang-loc-va-dieu-tri/